CRT Displays, Nostalgia & The Retro Games Aesthetic
Maybe you already had the impression that games were prettier in your childhood then they are now, and yes, indeed they were
Displays, Aesthetic, Retro
What will be discussed
In this article, we will explore the intertwined relationship between nostalgia and the impact of CRT displays on our perception of old games graphics. We will delve into the technical aspects of CRT technology, examining how it enhanced the visual appeal of pixel-based graphics. We will also contrast these qualities with the modern displays of today, investigating how their high-resolution and digital nature can alter our experience with video games.
We aim to understand why we remember old games graphics as being better than they look now. So, let us embark on this journey where the pixels of the past meet the screens of the present, and nostalgia intertwines with technology to shape our perception of gaming's golden era.
Nostalgia and Perception
Nostalgia has a peculiar way of coloring our memories, infusing them with a warm glow that seems to transcend the passage of time. This is evident in the realm of video games, specially for those who grew up during the heyday of gaming early years, there is often a sense of fondness and admiration for the games of old. We remember them as being more captivating, and even visually superior about how they look today.

Remembering old games graphics as being better than they actually are is a fascinating phenomenon that many people can relate to. Despite advancements in technology and the rise of visually stunning modern games, there is often a pervasive belief that the graphics of yesteryear possess a certain charm and appeal that surpasses what we see today. Several factors contribute to this phenomenon:
Nostalgic Bias: Nostalgia has a way of selectively enhancing our positive memories while downplaying the negative aspects. When we recall the games we played in our youth, we tend to focus on the joy and excitement they brought us, creating a nostalgic bias that elevates our perception of their graphics.
Emotional Attachment: The games we played during our childhood often hold a special place in our hearts. We associate them with cherished memories and carefree moments. This emotional attachment can significantly impact our perception of their graphics, as we subconsciously attribute positive emotions to the visual elements of these games.
Artistic Style: Older games often had distinct artistic styles driven by the technical limitations of the era. The pixelated graphics and vibrant color palettes employed by retro games have a unique aesthetic appeal that can evoke a sense of nostalgia. This distinctive style can influence how we remember and appreciate the graphics, even if objectively they may not match the realism or graphical fidelity of modern games.
It is essential to acknowledge that not everyone perceives old games graphics in the same way. Personal preferences, experiences, and exposure to different eras of gaming can all shape our individual perspectives. Nevertheless, the phenomenon of remembering old games graphics as superior serves as a testament to the enduring impact and emotional resonance that these games hold in our lives.
The Technological Influence
Is it just nostalgia playing tricks on our minds, or is there more to the story? While it is true that nostalgia plays a significant role in how we perceive the games of our youth, there is another factor at play - the influence of CRT monitors, those tube displays that once decorated our desks and living rooms.

In the era of CRT displays, gaming was a different experience altogether. The technology of those times gave rise to unique visual qualities that shaped the aesthetics of the games we played. The scanlines, pixel blending, and distinct color profiles of CRT monitors contributed to a look and feel that is still etched in the memories of many gamers.
The perception of old games graphics is not solely influenced by nostalgia and personal biases. The display technology of CRT monitors during the era of these games played a significant role in shaping how we remember and appreciate their visuals. The unique characteristics of CRT displays had a distinct impact on our perception.
Behind the CRT Displays
Cathode Ray Tube displays, employed a unique technology to render images. Understanding how they work, helps shed light on the distinctive visual qualities they offered.
The core component of a CRT display is the cathode ray tube itself. It consists of a vacuum-sealed glass tube with electron guns positioned at one end. These electron guns emit a stream of electrons towards the screen when energized.
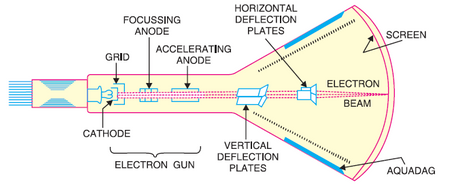
Once emitted, the stream of electrons is accelerated and focused using electromagnetic fields. The electron beam moves across the screen in a pattern, scanning line by line from top to bottom, and left to right. This scanning motion is crucial in creating the visual display.
The front of the CRT tube is coated with a phosphor material. When the electron beam strikes the phosphor-coated screen, it causes the phosphor to emit light. Each pixel on the screen corresponds to a tiny area coated with a specific color of phosphor.
To produce a wide range of colors, CRT displays employed an RGB (Red-Green-Blue) color scheme. By combining varying intensities of red, green, and blue phosphors, the display could create the illusion of different colors. Adjusting the intensity of the electron beam for each color component allowed for the creation of various shades and hues.
The electron beam repeatedly scans the entire screen at a specific rate, known as the refresh rate. The refresh rate is typically measured in hertz (Hz), indicating the number of times the screen is redrawn per second. Higher refresh rates resulted in smoother and flicker-free displays.
CRT monitors typically had higher refresh rates compared to modern displays up to the year of 2015, commonly with refresh rates of 60Hz, 75Hz, or even higher, depending on the specific model. This higher refresh rate was advantageous for fast-paced gaming and contributed to a smoother visual experience.
Through the combined interplay of these elements, CRT displays brought images to life with their characteristic qualities. The scanning motion, the phosphor-coated screen, and the RGB color scheme contributed to the distinct visual experience of CRT monitors. These technical aspects not only influenced how the graphics were displayed but also shaped our perception of the games visuals.
Scanlines, Pixel Blending, and Color Profiles
The appearance of game graphics was significantly influenced by three key characteristics of this technology: scanlines, pixel blending, and color profiles.
Scanlines: monitors displayed images by illuminating pixels row by row using a scanning electron beam. The visible gaps between these rows, known as scanlines, introduced a unique visual quality. The scanlines added separation between individual pixels, creating a clear distinction and enhancing the perceived sharpness of the graphics. This separation contributed to the overall crispness and definition of the images on CRT displays.
Pixel Blending: Due to the nature of this technology, adjacent pixels on the screen had some degree of blending. When colors met, they would blend together rather than appearing as distinct blocks. This pixel blending effect, often referred to as "pixel bloom" or "softening," smoothed out the transitions between colors and reduced the perceived blockiness of pixel-based graphics. As a result, the visuals appeared more cohesive and visually pleasing, adding a touch of elegance to the graphics.
Color Profiles: monitors had their own unique color profiles characterized by vibrant and saturated colors. These color profiles differed from the more accurate and natural color reproduction of modern displays. The CRT color profiles introduced a distinct visual aesthetic, infusing the graphics with bold and vibrant hues. This characteristic color rendering contributed to the overall visual charm and appeal of older games, setting them apart from the more realistic color reproduction of modern displays.

Together, scanlines, pixel blending, and color profiles played a pivotal role in shaping the appearance of graphics in older games. These characteristics offered a visual aesthetic that, when combined with the artistic choices of game developers, resulted in a distinct look and feel. Consequently, the graphics of old games on CRT monitors had a charm and appeal that is often fondly remembered.
Today Technology
Modern displays have come a long way since the era of CRT monitors. The advancements in display technology have brought about significant changes in how images are rendered. Understanding the technology behind contemporany screens provides valuable insights into how it influences the appearance of graphics in old games.
These advancements have led to several improvements, including higher resolutions, greater color accuracy, but also impressive refresh rates, that result in smoother motion. Common refresh rates for modern displays range from 60Hz to 240Hz, with higher rates becoming more prevalent in gaming-dedicated displays.

While these advancements have undoubtedly enhanced the visual experience for modern games, they also present a contrast to the unique qualities of CRT displays that influenced the appearance of graphics in older games.
Behind the LED Displays
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and LED (Light Emitting Diode) screens are two of the most popular display technologies in use today. In this article, we will specifically focus on the operation of LED screens.
LED displays operate based on the principle of light emission from individual light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Each LED is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it.
In an LED display, thousands or even millions of these individual LEDs are arranged in an array or grid pattern. The LEDs are typically grouped into clusters, with each cluster representing a single pixel on the display.
To create images and colors, the LEDs are controlled individually or in groups. By varying the intensity of the current flowing through the LEDs, different levels of brightness can be achieved. Additionally, LEDs can emit light in different colors, such as red, green, and blue (RGB), which can be combined to produce a wide range of colors.
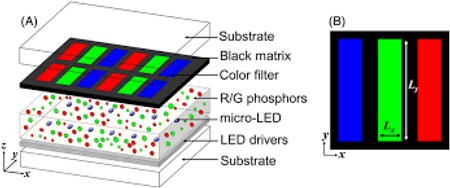
LED displays can be categorized into two types: direct-view LED displays and LED-backlit displays. For the purpose of this article, we will focus on LED-backlit displays, as direct-view LED displays are not commonly found in residential settings.
LED-backlit displays use a backlight system consisting of white LEDs positioned behind a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel. The LEDs provide illumination for the LCD panel, allowing it to control the passage of light and display the desired image or content. LED-backlit displays are commonly found in televisions, computer monitors, and smaller devices like smartphones and tablets.
Overall, the operation of LED displays relies on the precise control of individual LEDs or LED clusters to emit light, creating vibrant images and captivating visual experiences.
Yesterday Games, Today Technology
The high-resolution and digital nature of modern screens have a significant impact on the appearance of pixel-based graphics found in older games. Let's delve into how these factors influence the visual experience.

High Resolution: Modern displays typically have significantly higher resolutions compared to older CRT monitors. This increase in pixel density allows for sharper and more detailed images. However, when it comes to pixel-based graphics from older games, the higher resolution can sometimes work against their intended visual style.
a. Pixel Enlargement: When pixel-based graphics are displayed on high-resolution screens, each pixel of the original image is stretched across multiple pixels on the modern display. This enlargement can result in the loss of the distinctive blocky aesthetic that characterized older games. The once clearly defined pixels can become blurred or indistinct, altering the intended visual representation.
b. Lack of Authenticity: The high-resolution display can also expose the limitations and imperfections present in the original pixel-based graphics. The individual pixels, which were designed to be viewed on lower-resolution displays like CRT monitors, might reveal inconsistencies or irregularities when magnified on modern screens. This lack of authenticity can diminish the nostalgic charm associated with the original graphics.
Digital Nature: Modern screens are inherently digital in nature, operating with precise and quantized representations of visual data. This digital framework contrasts the analog nature of CRT displays, which had certain organic and imperfect qualities. The digital nature of modern screens can impact the appearance of pixel-based graphics in the following ways:
a. Loss of Analog Warmth: CRT displays possessed a unique warmth and character that was derived from their analog nature. The subtle variations in color and brightness lent a certain organic quality to the graphics. In contrast, the digital nature of modern screens can sometimes result in a more sterile and uniform appearance, potentially diluting the nostalgic essence associated with older games.
b. Sharpness and Clarity: The precise and digital rendering of graphics on modern screens can result in increased sharpness and clarity. While this can be advantageous for visually complex modern games, it can diminish the softer and more blended aesthetic of pixel-based graphics. The loss of the inherent analog softness can alter the intended visual experience.
As we explore the impact of high-resolution and digital nature on pixel-based graphics, we gain a deeper understanding of how the visual presentation of older games can be altered when viewed on modern displays. These factors contribute to the perception that the graphics of old games may not hold up to the idealized memories we have, further highlighting the role of nostalgia in our appreciation of their visuals.
Comparing Visuals
This comparison was made by wackoid.com
Mario Kart 64
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-20FS100

Final Fantasy 6
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-14AF1

Castlevania: Symphony of the Night
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-13M51

Mega Man 2
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-14AF1

Fatal Fury 3: Road to the Final Victory
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-13M51

Super Mario RPG
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-27S42

Final Fantasy 6
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-14AF1

Streets of Rage 2
Sharp Pixels vs. Sanyo DS-13320

Castlevania: Symphony of the Night
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-13M51

Final Fantasy 7
Sharp Pixels vs. Sony KV-14AF1

The Intersection of Nostalgia and CRT Displays
The distinct characteristics of CRT displays, as discussed earlier, contribute to the charm and aesthetic appeal of old games graphics. These qualities interact with nostalgia to further enhance our perception:
a. Nostalgic Aesthetic: The scanlines, pixel blending, and color profiles unique to CRT displays have become nostalgic aesthetics that we associate with the gaming experiences of the past. The presence of these characteristics on CRT monitors during the time we played these games has become intertwined with our memories and expectations.
b. Evoking a Sense of Authenticity: The CRT-specific qualities evoke a sense of authenticity, reminding us of the original hardware and gaming setups we used to enjoy. This authenticity contributes to the overall nostalgic experience, reinforcing the belief that the graphics were better during that time.
c. Enhancing Immersion: The CRT characteristics, such as the pronounced pixels and color vibrancy, had a particular impact on the immersion of gameplay. They contributed to a unique visual atmosphere that enhanced the overall gaming experience and drew us further into the virtual worlds of these games.

When nostalgia and the characteristics of CRT displays intersect, they reinforce each other, shaping our perception of old games graphics. The combined effect can create a powerful illusion that the graphics were superior, captivating, and more visually appealing than they might objectively appear on modern displays.
As we navigate the interplay between nostalgia and CRT display characteristics, we gain insights into why we remember the graphics of old games as better than they actually are. Understanding this complex interaction allows us to appreciate the unique appeal of retro gaming and the role of personal experiences in shaping our perception of visuals.
Acknowledging Subjectivity and Individual Experiences
It's important to recognize that the phenomenon of remembering old games graphics as “better than they actually are” is subjective and can vary from person to person. Individual experiences and personal preferences play a significant role in shaping our perception of graphics:
Personal Preferences: Each individual has their own preferences when it comes to visual aesthetics. Some may prefer the crispness and clarity of modern displays, while others may have a strong affinity for the nostalgic charm of CRT monitors. These preferences can greatly influence how one perceives and appreciates the graphics of old games.
Context and Exposure: The context in which we experienced old games also plays a role. Factors such as the quality of the display we originally played on, the specific games we played, and the overall gaming atmosphere at the time can all shape our perception. Someone who grew up playing games on CRT displays may have a stronger attachment to that visual style compared to someone who primarily experienced modern displays.
Nostalgic Associations: The nostalgic associations we have with old games graphics go beyond just the visual aspect. They are intertwined with memories, emotions, and the overall experience of playing those games. These associations can significantly influence how we remember and perceive the graphics, as they become inseparable from the larger gaming experience.
Changing Expectations: As technology advances, our expectations for graphics and visual fidelity evolve as well. What was considered impressive or cutting-edge in the past may not meet the standards of today's high-definition and realistic visuals. Our perception of old games graphics can be influenced by the changing expectations we have as a result of exposure to modern graphics.
It's essential to recognize that the perception of old games graphics is subjective and influenced by a range of factors. While some may genuinely prefer the visuals of older games, others may acknowledge the limitations and appreciate them within the context of their time. The subjective nature of this phenomenon allows for diverse opinions and interpretations, adding to the richness of discussions surrounding retro gaming and nostalgia.
Understanding the subjective nature of how we remember and perceive old games graphics encourages us to embrace and respect different perspectives. It highlights the importance of personal experiences, preferences, and the interplay between nostalgia and display technologies in shaping our perception of visual aesthetics in gaming.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the phenomenon of remembering old games graphics as being better than they actually are. We discussed how this perception may be influenced by the display technology of CRT monitors, including scanlines, pixel blending, and color profiles. We also explained the technology behind modern displays and how their high resolution and digital nature can impact the appearance of pixel-based graphics.
We then delved into how nostalgia and the characteristics of CRT displays intersect to influence our perception of old games graphics. We acknowledged the subjective nature of this phenomenon and how individual experiences can differ. Additionally, we mentioned the ongoing appeal of old games and the influence of nostalgia on game design.
Overall, it is clear that nostalgia plays a significant role in the enjoyment of old games. While modern displays may not replicate the experience of CRT monitors, nostalgia can add to the enjoyment of gaming and make the experience richer and more meaningful.
As someone who grew up playing old games on CRT monitors, I can personally attest to the power of nostalgia. Even today, when I revisit those games on modern displays, I can't help but feel a sense of nostalgia and appreciation for the way they looked and played. Ultimately, nostalgia is a powerful force that can enhance our appreciation for the past while also influencing the way we perceive the present.
